hyeonga_code
Java의 신_Chapter 02_Hello God of Java 본문
2024.03.26
윈도우 커맨드 창에서 java / javac 입력 시 사용 설명 출력되지 않는 경우 >> JDK 설치하기
> java
C:\Users\hyeonga> java
Usage: java [options] <mainclass> [args...]
(to execute a class)
or java [options] -jar <jarfile> [args...]
(to execute a jar file)
or java [options] -m <module>[/<mainclass>] [args...]
java [options] --module <module>[/<mainclass>] [args...]
(to execute the main class in a module)
or java [options] <sourcefile> [args]
(to execute a single source-file program)
Arguments following the main class, source file, -jar <jarfile>,
-m or --module <module>/<mainclass> are passed as the arguments to
main class.
where options include:
-cp <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
-classpath <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
--class-path <class search path of directories and zip/jar files>
A ; separated list of directories, JAR archives,
and ZIP archives to search for class files.
-p <module path>
--module-path <module path>...
A ; separated list of directories, each directory
is a directory of modules.
--upgrade-module-path <module path>...
A ; separated list of directories, each directory
is a directory of modules that replace upgradeable
modules in the runtime image
--add-modules <module name>[,<module name>...]
root modules to resolve in addition to the initial module.
<module name> can also be ALL-DEFAULT, ALL-SYSTEM,
ALL-MODULE-PATH.
--list-modules
list observable modules and exit
-d <module name>
--describe-module <module name>
describe a module and exit
--dry-run create VM and load main class but do not execute main method.
The --dry-run option may be useful for validating the
command-line options such as the module system configuration.
--validate-modules
validate all modules and exit
The --validate-modules option may be useful for finding
conflicts and other errors with modules on the module path.
-D<name>=<value>
set a system property
-verbose:[class|module|gc|jni]
enable verbose output
-version print product version to the error stream and exit
--version print product version to the output stream and exit
-showversion print product version to the error stream and continue
--show-version
print product version to the output stream and continue
--show-module-resolution
show module resolution output during startup
-? -h -help
print this help message to the error stream
--help print this help message to the output stream
-X print help on extra options to the error stream
--help-extra print help on extra options to the output stream
-ea[:<packagename>...|:<classname>]
-enableassertions[:<packagename>...|:<classname>]
enable assertions with specified granularity
-da[:<packagename>...|:<classname>]
-disableassertions[:<packagename>...|:<classname>]
disable assertions with specified granularity
-esa | -enablesystemassertions
enable system assertions
-dsa | -disablesystemassertions
disable system assertions
-agentlib:<libname>[=<options>]
load native agent library <libname>, e.g. -agentlib:jdwp
see also -agentlib:jdwp=help
-agentpath:<pathname>[=<options>]
load native agent library by full pathname
-javaagent:<jarpath>[=<options>]
load Java programming language agent, see java.lang.instrument
-splash:<imagepath>
show splash screen with specified image
HiDPI scaled images are automatically supported and used
if available. The unscaled image filename, e.g. image.ext,
should always be passed as the argument to the -splash option.
The most appropriate scaled image provided will be picked up
automatically.
See the SplashScreen API documentation for more information
@argument files
one or more argument files containing options
-disable-@files
prevent further argument file expansion
--enable-preview
allow classes to depend on preview features of this release
To specify an argument for a long option, you can use --<name>=<value> or
--<name> <value>.
> javac
C:\Users\hyeonga> javac
Usage: javac <options> <source files>
where possible options include:
@<filename> Read options and filenames from file
-Akey[=value] Options to pass to annotation processors
--add-modules <module>(,<module>)*
Root modules to resolve in addition to the initial modules, or all modules
on the module path if <module> is ALL-MODULE-PATH.
--boot-class-path <path>, -bootclasspath <path>
Override location of bootstrap class files
--class-path <path>, -classpath <path>, -cp <path>
Specify where to find user class files and annotation processors
-d <directory> Specify where to place generated class files
-deprecation
Output source locations where deprecated APIs are used
--enable-preview
Enable preview language features. To be used in conjunction with either -source or --release.
-encoding <encoding> Specify character encoding used by source files
-endorseddirs <dirs> Override location of endorsed standards path
-extdirs <dirs> Override location of installed extensions
-g Generate all debugging info
-g:{lines,vars,source} Generate only some debugging info
-g:none Generate no debugging info
-h <directory>
Specify where to place generated native header files
--help, -help, -? Print this help message
--help-extra, -X Print help on extra options
-implicit:{none,class}
Specify whether or not to generate class files for implicitly referenced files
-J<flag> Pass <flag> directly to the runtime system
--limit-modules <module>(,<module>)*
Limit the universe of observable modules
--module <module-name>, -m <module-name>
Compile only the specified module, check timestamps
--module-path <path>, -p <path>
Specify where to find application modules
--module-source-path <module-source-path>
Specify where to find input source files for multiple modules
--module-version <version>
Specify version of modules that are being compiled
-nowarn Generate no warnings
-parameters
Generate metadata for reflection on method parameters
-proc:{none,only}
Control whether annotation processing and/or compilation is done.
-processor <class1>[,<class2>,<class3>...]
Names of the annotation processors to run; bypasses default discovery process
--processor-module-path <path>
Specify a module path where to find annotation processors
--processor-path <path>, -processorpath <path>
Specify where to find annotation processors
-profile <profile>
Check that API used is available in the specified profile
--release <release>
Compile for a specific VM version. Supported targets: 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11
-s <directory> Specify where to place generated source files
-source <release>
Provide source compatibility with specified release
--source-path <path>, -sourcepath <path>
Specify where to find input source files
--system <jdk>|none Override location of system modules
-target <release> Generate class files for specific VM version
--upgrade-module-path <path>
Override location of upgradeable modules
-verbose Output messages about what the compiler is doing
--version, -version Version information
-Werror Terminate compilation if warnings occur
설치된 java 버전 확인하기
> java -version
C:\Users\hyeonga> java -version
java version "11.0.20" 2023-07-18 LTS
Java(TM) SE Runtime Environment 18.9 (build 11.0.20+9-LTS-256)
Java HotSpot(TM) 64-Bit Server VM 18.9 (build 11.0.20+9-LTS-256, mixed mode)
-- cmd에서 java 프로그램이 실행되는 이유
---- Program Files > Java > jdk 폴더 > bin 폴더 내에 수많은 .exe 파일(실행파일)
------ 리눅스/맥에는 없음
---- exe 파일이 있는 경로를 Path에서 찾아 자동으로 실행
-- 윈도우에 지정되어 있는 Path를 확인하는 방법
> set %PATH%
C:\Users\hyeon> set %PATH%
C:\Program Files\Java\jdk-11.0.20\bin;
콘솔창에서 java 실행하기
1) 작업 폴더 생성하기
2) 파일 작성하기_메모장으로 작업
HelloGodOfJava.java
public class HelloGodOfJava{
}
3) 콘솔창에서 작업 폴더로 이동하기
C:\> cd C:\godofjava
4) 파일 존재 여부 확인하기
> dir
C:\godofjava> dir
C:\godofjava 디렉터리
2024-03-26 오후 01:35 <DIR> .
2024-03-26 오후 01:35 33 HelloGodOfJava.java
1개 파일 33 바이트
1개 디렉터리 112,195,006,464 바이트 남음
5) 컴파일하기
C:\godofjava> javac HelloGodOfJava.java
C:\godofjava>
>>> .class 파일 생성됨
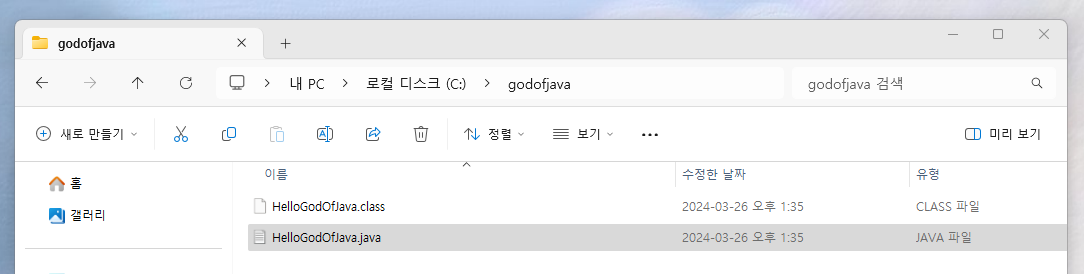
C:\godofjava> dir
C:\godofjava 디렉터리
2024-03-26 오후 01:35 <DIR> .
2024-03-26 오후 01:35 202 HelloGodOfJava.class
2024-03-26 오후 01:35 33 HelloGodOfJava.java
2개 파일 235 바이트
1개 디렉터리 112,192,937,984 바이트 남음
---- 파일이 존재하지 않는 경우
> javac NoSearchFile.java
C:\godofjava> javac NoSearchFile.java
error: file not found: NoSearchFile.java
Usage: javac <options> <source files>
use --help for a list of possible options
6) 실행하기
> java HelloGodOfJava
C:\godofjava> java HelloGodOfJava
Error: Main method not found in class HelloGodOfJava, please define the main method as:
public static void main(String[] args)
or a JavaFX application class must extend javafx.application.Application-- 메인 메소드가 없어 오류가 발생
---- 실행을 목적으로 하는 모든 자바 클래스는 main() 메소드가 반드시 존재해야 한다.
---- 존재하지 않는 클래스를 실행하는 경우
> java NoSearchFile
C:\godofjava> java NoSearchFile
Error: Could not find or load main class NoSearchFile
Caused by: java.lang.ClassNotFoundException: NoSearchFile
>> 메인 메소드 선언하기
public class HelloGodOfJava{
// main method
public static void main(String[] args){
/*
public : 접근제어자
static : 객체를 생성하지 않아도 호출할 수 있다
void : 반환값이 없다
main : 메소드 이름(대/소문자 구분)
(String[] args) : 매개변수 (args는 변경 가능)
*/
System.out.println("Hello God of Java!!!");
}
}
>>> 컴파일
> javac HelloGodOfJava.java
C:\godofjava> javac HelloGodOfJava.java
C:\godofjava>
>>> 실행
> java HelloGodOfJava
C:\godofjava> java HelloGodOfJava
Hello God of Java!!!
C:\godofjava>
-- System.out.println()
1) 출력 문자 추가하기
public class HelloGodOfJava{
// main method
public static void main(String[] args){
/*
public : 접근제어자
static : 객체를 생성하지 않아도 호출할 수 있다
void : 반환값이 없다
main : 메소드 이름(대/소문자 구분)
(String[] args) : 매개변수 (args는 변경 가능)
*/
System.out.println("Hello God of Java!!!");
System.out.println("Hello Seoul~~");
System.out.print("SeoulSeoul :) ");
System.out.print(" Seoul :)");
}
}
>>> 컴파일
> javac HelloGodOfJava.java
C:\godofjava> javac HelloGodOfJava.java
C:\godofjava>
>>> 실행
> java HelloGodOfJava
C:\godofjava> java HelloGodOfJava
Hello God of Java!!!
Hello Seoul~~
SeoulSeoul :) Seoul :)
C:\godofjava>
-- 주석
// 한 줄 주석
줄이 바뀌면 주석처리가 안됩니다.
/*
여러 줄 주석
줄이 바뀌어도 주석처리가 됩니다.
*/
/**
문서용 주석_documentation comment
클래스 선언/메소드 선언 바로 앞에 있는 경우
*/
-- Calculator.java 작성
public class Calculator{
public static void main(String[] args){
System.out.println("Calculator class started");
System.out.println("add(4,2) : " + add(4,2));
System.out.println("addAll(4,2,1) : " + addAll(4,2,1));
System.out.println("subtract(4,2) : " + subtract(4,2));
System.out.println("multiply(4,2) : " + multiply(4,2));
System.out.println("divide(4,2) : " + divide(4,2));
}
public static int add(int num1, int num2){
return num1 + num2;
}
public static int addAll(int num1, int num2, int num3){
return num1 + num2 + num3;
}
public static int subtract(int num1, int num2){
return num1 - num2;
}
public static int multiply(int num1, int num2){
return num1 * num2;
}
public static int divide(int num1, int num2){
return num1 / num2;
}
}
>>> 컴파일
> javac Calculator.java
C:\godofjava>javac Calculator.java
C:\godofjava>
>>> 실행하기
> java Calculator
C:\godofjava> java Calculator
Calculator class started
add(4,2) : 6
addAll(4,2,1) : 7
subtract(4,2) : 2
multiply(4,2) : 8
divide(4,2) : 2
정리하기
1. main() 메소드의 메소드 이름 앞에 작성되어야 하는 예약어
-- public static void
---- public : 어떤 클래스에서도 접근이 가능
---- static : 객체를 생성하지 않아도 접근 가능한 메소드
---- void : 리턴 값이 없음
2. main() 메소드의 매개변수
-- String[] args
3. 클래스에 main() 메소드가 없는 경우 java 명령어로 클래스를 수행할 수 없다.
4. System.out.println() 메소드는 콘솔 창에 한 줄 출력의 용도로 사용된다.
5. System.out.print() 메소드는 System.out.println() 메소드와 다르게 줄 바꿈이 없이 출력된다.
---- 줄바꿈을 하지 않기 때문에 이 메소드 호출 후에 출력 메소드를 호출하는 경우 같은 줄에 결과가 출력된다.
6. // 는 한 줄 주석 처리 기호
7. /* 로 시작하고 */ 로 끝나는 사이에 있는 소스는 여러 줄이 주석처리 되어 컴파일 시 무시된다.
---- 블록 주석으로, 해당 블록 내의 모든 내용은 무시된다.
8. 메소드를 선언할 때 반드시 꼭 있어야 하는 것은
-- 리턴 타입, 메소드 이름, 메소드 내용
'Java' 카테고리의 다른 글
| Java의 신_Chapter 03_Object (0) | 2024.03.27 |
|---|---|
| Java의 신_Chapter 02_jshell 활용하기 (0) | 2024.03.27 |
| Java의 신_Chapter 01_Programming (0) | 2024.03.27 |
| Java_로또 기능 작성하기 (0) | 2023.10.31 |
| Java_룸 예약 시스템 작성하기 (0) | 2023.10.31 |




